Understanding CDNs: Enhancing File Delivery for Developers

CDNs (Content Delivery Networks) are essential for delivering digital content quickly and efficiently. They work by caching files like videos, images, and scripts on servers located closer to users, reducing load times and improving reliability. This global network of edge servers ensures faster access, minimizes server overload, and cuts bandwidth costs. CDNs also provide security features like DDoS protection and SSL encryption, making them a critical tool for modern web development.
Key Benefits of CDNs:
- Faster Load Times: Cache content near users, reducing latency by up to 83%.
- Improved Scalability: Handle traffic surges with load balancing and failover systems.
- Reduced Costs: Lower bandwidth usage by serving cached content.
- Enhanced Security: Protect against attacks with built-in features.
For developers, CDNs simplify file delivery through caching strategies, compression, and dynamic content management. Tools like Simple File Upload offer prebuilt solutions to integrate CDNs seamlessly into projects, saving time and effort while ensuring global performance.
CDNs 101: An Introduction to Content Delivery Networks - Jake Ginnivan - NDC Oslo 2023

How CDNs Work in File Upload and Delivery
CDNs rely on interconnected components to ensure files are delivered quickly and reliably. This system works behind the scenes to make sure your files reach users as efficiently as possible.
CDN Architecture Components
At the heart of a CDN are three key components that work together to streamline content delivery. First, edge servers play a crucial role. These servers are strategically located at Points of Presence (PoPs) around the globe, caching content closer to users to minimize the distance data has to travel.
Next is the origin server, which stores the original version of your files. When edge servers don't have the requested content cached, they fetch it from this central source. To keep things running smoothly, load balancers distribute traffic across servers, preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed.
CDNs also include failover systems to ensure uninterrupted service. For example, Anycast routing redirects traffic to an alternative data center if a server experiences technical issues.
Modern CDNs take performance a step further with cache tiers. Features like Smart Tiered Cache route cache requests through an optimized upper tier, which increases cache hit rates and reduces the load on origin servers. This system uses real-time performance and routing data to identify the best upper-tier location for your content.
Together, these components form a robust framework for managing file uploads and delivering content effectively.
File Upload and Delivery Process
CDNs handle file distribution through two main methods: pushing and pulling. In a push setup, you proactively upload content to the CDN, giving you control over what gets cached and when. With pulling, the CDN automatically retrieves content from your origin server when it’s not already cached.
Here’s how it works when a user requests a file: The request is routed to the nearest edge server based on the user’s location. If the file is already cached on the edge server (a cache hit), it’s delivered immediately. If not (a cache miss), the edge server fetches the file from the origin server and caches it for future requests.
This process dramatically reduces latency. Research shows that CDNs can cut website latency by an average of 83% compared to sites without a CDN. Considering that a mere 1-second delay in load time can lead to a 7% drop in conversions, the impact on business performance is undeniable.
CDNs also use an Origin Shield layer to protect origin servers from being overwhelmed by high traffic during cache misses. This extra caching layer between edge servers and the origin server further optimizes the delivery process.
Cache Management and Optimization
Once files are delivered, maintaining efficient caching is key to ensuring speed and reliability. Time-to-Live (TTL) settings dictate how long content remains cached before it expires. When a cached file expires, the CDN fetches a fresh copy from the origin server the next time it’s requested.
Sometimes, you need to update content immediately. That’s where cache invalidation comes into play. You can use purging to manually remove specific files from the cache or refreshing to update cached content with the latest version from the origin server.
Headers like Cache-Control and Expires are essential for optimizing performance. These headers guide the CDN on how to handle your content, ensuring frequently accessed files remain cached at edge servers. Here’s a quick breakdown of key cache control parameters:
| Parameter | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Max-Age | Sets the maximum time (in seconds) a resource stays fresh | Ideal for static resources |
| S-Maxage | Similar to Max-Age but for shared caches | Used for CDN or intermediary caches |
| Must-Revalidate | Ensures caches revalidate content once it becomes stale | For serving updated content |
| No-Cache | Requires cache validation before use | Best for dynamic content |
| No-Store | Prevents caching altogether | Suitable for sensitive or personal data |
| Public/Private | Determines if content is cacheable by shared caches or user-specific | Balances general and personalized content |
CDNs also improve delivery speeds through compression techniques. For example, GZip compression can shrink file sizes by 50% to 70%. Additionally, using solid-state drives (SSDs) allows files to be accessed up to 30% faster than traditional hard drives. These optimizations work together to enhance the user experience.
With 63% of the top 10,000 websites relying on CDNs, it’s clear that developers see their value in modern web applications. By combining smart caching, advanced routing, and efficient file delivery, CDNs have become a cornerstone of fast and reliable web performance.
Next, we’ll dive into how these CDN capabilities integrate seamlessly into development workflows.
Key Benefits of CDNs for Developers
CDNs bring a range of advantages that directly impact both user experience and the efficiency of development operations. By understanding these benefits, developers can make smarter decisions when incorporating CDNs into their projects.
Better Performance and Reduced Latency
CDNs improve performance by reducing the physical distance between users and the content they access. Cached files are stored on edge servers around the globe, allowing users to retrieve data from servers closer to their location instead of distant origin servers. This setup can cut latency by as much as 60% in applications like online gaming.
But it’s not just about proximity. CDNs utilize advanced technologies like solid-state drives, HTTP/2, and QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections). They also apply compression techniques that shrink file sizes by 50% to 70%, speeding up downloads and lowering bandwidth usage.
The impact of faster load times is clear. Research indicates that even a one-second delay can result in a 7% drop in conversions. For example, one retailer facing high bounce rates during peak shopping periods implemented CDN features like static asset caching and HTTP/2. This reduced page load times by 40% and boosted sales by 15%.
For time-sensitive applications, the industry recommends keeping latency under 50ms for ideal performance, with anything under 100ms being generally acceptable. Latency above 100ms, however, could harm real-time functionality. Now, let’s look at how CDNs manage heavy traffic while maintaining availability.
Better Scalability and Availability
CDNs aren’t just about speed - they also deliver scalability and reliable availability. With the ability to handle over 100 Tbps of traffic, CDNs ensure content stays accessible even during massive surges in demand. Load balancing spreads traffic across multiple servers, preventing overloads that could lead to downtime.
Geographic distribution plays a critical role here. Setting up regional endpoints can reduce latency by 40–70% compared to relying on a single-region setup. For instance, a video platform used optimized edge placement and adaptive bitrate streaming during live events, cutting buffering by 60%.
CDNs also improve reliability through automatic failover mechanisms. If an origin server goes down, traffic is rerouted to operational servers, ensuring uninterrupted availability.
Security and Cost Benefits
CDNs do more than just enhance performance - they also strengthen security and reduce costs. Built-in features like DDoS protection, SSL/TLS encryption, bot management, and origin shielding help safeguard your infrastructure. Origin shielding, in particular, not only protects servers from direct attacks but also reduces the load on them.
From a cost perspective, CDNs help by caching content and reducing the number of requests sent to origin servers. This decreases bandwidth usage, which can lead to lower hosting expenses and infrastructure needs. The growing adoption of CDNs reflects these benefits, with the market valued at $21.67 billion in 2023 and projected to hit $140.73 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 21.1%.
"You don't need to cache everything: You need to cache the things that most people use most of the time."
- Artur Bergman, Fastly founder and CTO
A global SaaS provider struggling with slow response times for users in remote areas switched to a CDN with a larger global network and optimized DNS resolution. This reduced latency by 50% and significantly improved user satisfaction.
CDNs also offer flexible pricing models, such as pay-as-you-go, committed contracts, tiered pricing, and location-based pricing. Pay-as-you-go works well for unpredictable traffic, while committed contracts are better suited for steady traffic patterns, offering cost savings.
Modern CDNs are evolving, adding features like API management, distributed security, and even AI processing at the edge. By consolidating these services, developers can simplify operations and potentially cut costs.
The connection between speed and conversions is undeniable. A website loading in 2.4 seconds might achieve a 1.9% conversion rate, but at 3.3 seconds, that rate drops to 1.5%. By the time load times hit 4.2 seconds, conversions fall below 1%, and at 5.7 seconds, they plummet to less than 0.6%.
Adding CDNs to Development Workflows
To effectively integrate CDNs into your development process, you’ll need to set up endpoints, configure caching strategies, and adapt your framework to work seamlessly with the CDN. Let’s break down these steps.
Setting Up CDN Endpoints
The first step is selecting a CDN provider that aligns with your needs for speed, security, and global coverage. After that, use tools like Terraform to streamline the endpoint configuration process and reduce the risk of manual errors. Ensure your chosen CDN is compatible with your current hosting setup to avoid unexpected issues.
Here’s an example of setting up endpoints using Azure CDN with C# .NET 8:
- Start by creating a Blob Storage account in the Azure portal.
- Set up a Blob Container for your static files, such as images or videos.
-
Create a CDN Profile and select an appropriate SKU type (e.g.,
Standard_Microsoft), then link the profile to your Blob Storage as the origin. -
Finally, create an endpoint within the CDN Profile. This endpoint allows your files to be served through URLs like
https://my-cdn.azureedge.net/images/logo.png.
To complete the setup, update your DNS CNAME records to point to your CDN’s domain and restrict access to your origin server by allowing only the CDN’s IP ranges.
Configuring Cache Control and Performance Monitoring
Setting proper cache control headers and monitoring your CDN’s performance are crucial for a smooth user experience. Use Cache-Control headers with max-age to specify how long content should be cached. For shared caches, the s-maxage directive takes precedence over max-age. For dynamic content, consider options like stale-while-revalidate or stale-if-error to ensure users can access content even if the origin server is temporarily unavailable.
| Technique | Implementation Complexity | Reliability | CDN Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filename Revisioning | Requires build integration | Minimizes caching issues | Excellent |
| Query Parameters | Easy to append manually | Less consistent | Good |
| Cache-Control Headers | Configuration-based | Depends on server/CDN | Excellent |
To avoid cache-busting issues, version your static assets using filename revisioning. For example, instead of app.css?v=2.0, rename the file to app-v2.0.css. This method works more reliably across different CDNs. When updating content, upload a new version rather than modifying the existing file. If changes are unavoidable, make them atomic to ensure consistency.
During high-traffic periods, extend cache durations and configure the CDN to serve stale content temporarily. Regularly check CDN logs to identify potential bottlenecks early and adjust your settings as needed.
Practical Implementation Examples
With endpoints and caching configured, integrate CDN usage into your framework-specific workflows. Modern frameworks make this straightforward. For instance:
-
In React, you can prefix static asset URLs in
package.json. -
Angular supports the
--deploy-urlflag for CDN integration. -
Vue allows you to set the
publicPathoption for similar purposes.
For file uploads, store them directly in your origin storage and let the CDN cache them as needed. For example, CloudFront operates as a pull CDN, caching content based on user requests, which is ideal for handling user-generated content.
To further optimize delivery, use techniques like bundling, minification, and gzip compression. If your application is mission-critical, consider a multi-CDN strategy to ensure redundancy and reliability.
"In the realms of web performance and security, a well-implemented CDN isn't just an option; it's an indispensable asset for any business online."
- Ciaran Connolly, Founder, ProfileTree
For even better performance, enable TLS early data, which can boost resumed connection rates by 30% to 50%. Ensure your CDN supports HTTP/3 and QUIC protocols to take advantage of these improvements. Regularly reviewing and tweaking your CDN settings will help you stay ahead of performance challenges and leverage the latest advancements in CDN technology.
Using Simple File Upload's Global CDN for File Delivery
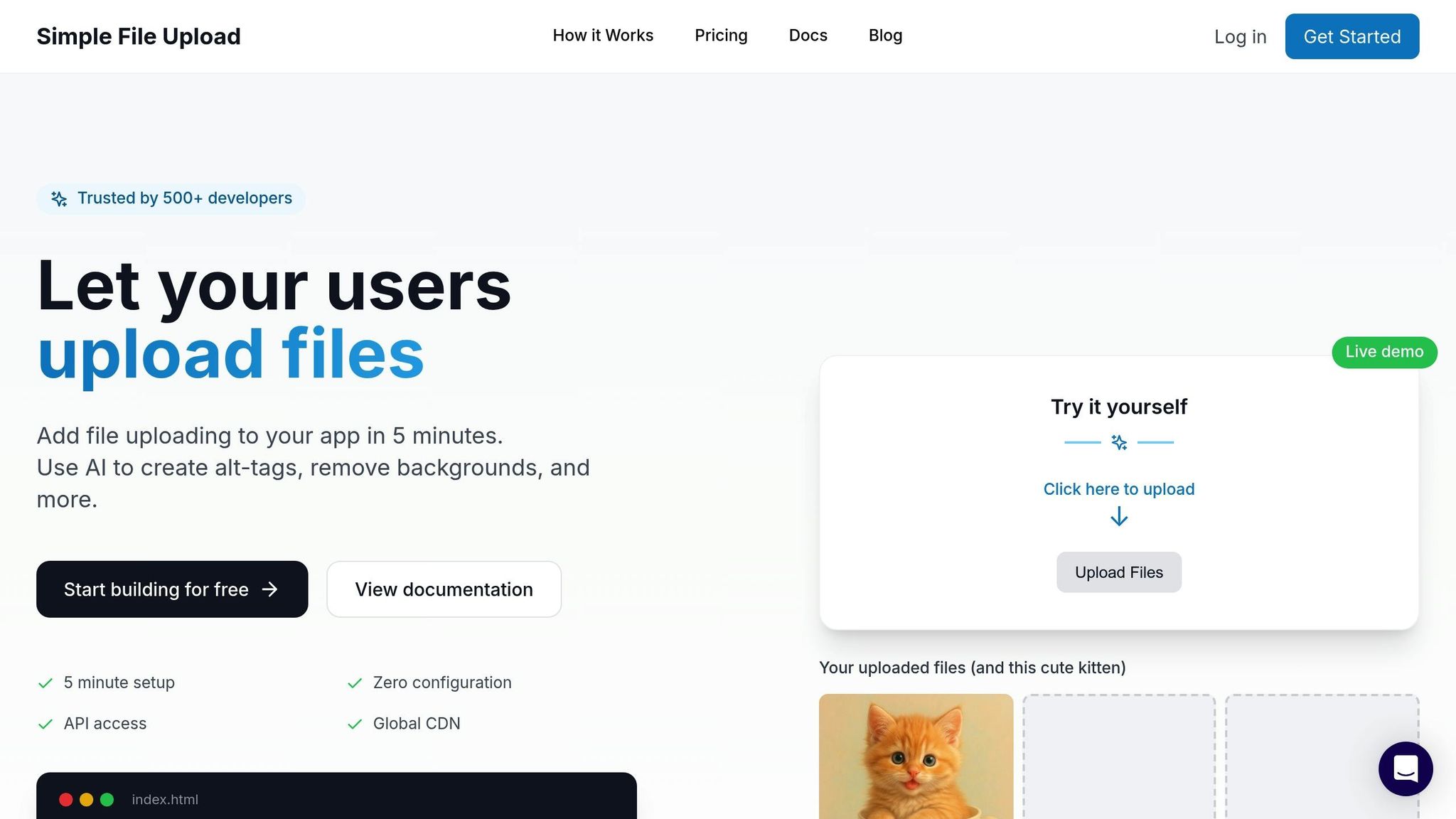
Simple File Upload simplifies global file delivery by incorporating a built-in CDN solution, eliminating the need to manage the complexities of creating your own. Trusted by over 500 developers, this platform streamlines everything from file uploads to worldwide distribution, saving time and effort.
Core Features of Simple File Upload's CDN
Simple File Upload's CDN uses 200+ edge locations globally, ensuring fast file loading no matter where users are located. But it doesn't stop at basic delivery - it includes a range of features to enhance functionality.
The prebuilt uploader is easy to integrate into any application and customizable with attributes like multiple, max-files, and max-file-size. For React users, the simple-file-upload-react package makes integration even smoother.
On-demand image transformations allow resizing, cropping, and optimizing images through simple URL parameters (e.g., ?w=200&h=200). This approach eliminates the need to store multiple versions of the same image, which saves storage space while maintaining quick delivery.
The platform also includes AI-powered tools like automatic alt-text generation and background removal. These features improve accessibility and reduce manual tasks. Additionally, direct file uploads send files straight from the user's browser to cloud storage, bypassing your server entirely. This is especially useful for platforms like Heroku, which rely on ephemeral filesystems.
"Simple File Upload allowed my team to stop fighting with file uploading and focus on what matters – our customers. We had the uploader up and running in 5 minutes! It really is that easy!"
– Drew Clemens, Founder, Protege.dev
Pricing and Storage Options
Simple File Upload offers flexible pricing plans to match different project needs:
| Plan | Monthly Price | Storage | Max File Size | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | $35 | 25 GB | 5 MB | Prebuilt uploader, CDN delivery, direct uploads |
| Pro | $80 | 100 GB | 50 MB | Larger storage and file limits, all Basic features |
| Custom | $250 | 500 GB | 50 MB | Redundant storage, one-on-one support |
The Custom plan provides added protection with redundancy across two storage providers and includes personalized customer support. Regardless of the plan, the global CDN is included at no extra cost, ensuring predictable costs even during traffic surges.
Developer Productivity and Integration
Simple File Upload is compatible with a wide range of frameworks and programming languages, including React, Vue, Angular, JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, Ruby, PHP, Go, Rust, and Java. This versatility means you can use the same solution across multiple projects and tech stacks.
For projects using vanilla JavaScript, you can include the library via CDN and embed the <simple-file-upload> web component to handle uploads effortlessly. The component automatically manages the process while providing CDN URLs through JavaScript events.
By skipping the need for AWS configurations - like setting up IAM policies, S3 buckets, or CORS rules - Simple File Upload allows developers to focus on building features that directly impact users.
"Simplify your file handling"
– Robin Warren, Chief Dogsbody, Cherry Wood Software
Installation is straightforward: use npm or yarn to add the library, integrate the uploader component, and capture upload events to retrieve CDN URLs. The platform takes care of security, scaling, and global delivery.
For image-heavy applications, the dynamic resizing feature optimizes performance by generating image sizes on demand via URL parameters. This reduces storage costs and speeds up uploads, aligning perfectly with the platform's focus on performance and scalability.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways on CDNs and File Delivery
CDNs play a crucial role in modern web development, transforming how files are delivered and accessed. By implementing CDNs, websites can achieve up to 50% faster load times, which directly contributes to improved user experiences and increased customer satisfaction. These speed boosts also bring a host of operational benefits.
In addition to faster performance, CDNs provide enhanced security and cost savings by caching content closer to users . For developers, CDNs offer critical advantages like improved availability and redundancy, ensuring smooth handling of traffic surges and minimizing the impact of server outages. This level of reliability is especially important for applications that need consistent performance across global audiences.
The growing adoption of CDNs highlights their value in today’s development landscape. However, traditional CDN setups can be challenging, often requiring intricate configurations that slow down development workflows.
Simple File Upload addresses these hurdles with a fully managed CDN solution designed to streamline the setup process. Its ability to integrate effortlessly with various frameworks and programming languages allows developers to maintain uniformity across projects. Features like AI-powered alt-text generation and image transformations add even more functionality.
With transparent pricing, built-in security measures, and straightforward integration, CDN technology is now within reach for development teams of any size. As the demand for fast and reliable file delivery continues to grow, leveraging CDNs has become a necessity for creating competitive web applications.
FAQs
How do CDNs help improve website security with features like DDoS protection and SSL encryption?
CDNs play a crucial role in keeping websites secure by incorporating features like DDoS protection and SSL encryption. Here's how they work:
DDoS protection helps mitigate attacks by spreading incoming traffic across multiple servers. This prevents malicious attempts or sudden traffic spikes from overwhelming a website and causing downtime.
On top of that, SSL/TLS encryption secures the data exchanged between users and servers. By encrypting this information, CDNs help shield sensitive data from risks like breaches or man-in-the-middle attacks. This not only protects the website but also strengthens user confidence.
With these built-in security features, CDNs become a go-to solution for developers who want to protect their projects while ensuring a seamless and secure experience for users.
What’s the difference between pull and push CDNs, and how do they affect content delivery?
When using a pull CDN, content is automatically fetched from the origin server the first time a user requests it. While this can cause a slight delay during the initial load, it simplifies management for content that's accessed frequently. This makes pull CDNs a great fit for handling dynamic or unpredictable traffic patterns.
In contrast, a push CDN requires you to manually upload content to edge servers. This setup delivers faster performance for files that have already been distributed but involves more hands-on management. Push CDNs work best for static or large files that experience consistent demand.
Deciding between a pull or push CDN comes down to the specific needs of your project. Pull CDNs are simpler to implement and maintain, while push CDNs provide greater control and are ideal for predictable, high-demand content.
How can developers seamlessly integrate CDNs into their workflows to boost file delivery speed and performance?
To make the most of CDNs in your development workflow, focus on automating key tasks like cache invalidation and content updates. This ensures your files remain current without manual intervention. Adding performance monitoring tools is another smart move - they help pinpoint latency problems and fine-tune delivery for your users.
You can also integrate CDN configurations directly into your deployment pipeline. This simplifies updates and keeps performance steady. Features like load balancing and geo-routing are particularly useful for managing traffic surges and improving scalability. By syncing CDN management with your development processes, you’ll boost delivery speed, reliability, and the overall experience for your users.
Related Blog Posts
Ready to simplify uploads?
Join thousands of developers who trust Simple File Upload for seamless integration.